流程图 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 ┌ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ┐ 第一阶段:Launcher 处理 Launcher.startActivity() ↓ ActivityTaskManager.startActivity() ↓ (Binder 跨进程) ActivityManagerService.startActivity() └ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ┘ ↓ ┌ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ┐ 第二阶段:进程创建 Process.start() ↓ ZygoteProcess.start() ↓ Zygote.fork() ↓ ActivityThread.main() └ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ┘ ↓ ┌ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ┐ 第三阶段:SO 加载 LoadedApk.loadLibrary() ↓ System.loadLibrary() ↓ Runtime.loadLibrary0() ↓ DexPathList.findLibrary() └ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ┘ ↓ ┌ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ┐ 第四阶段:DEX 加载 PathClassLoader.loadClass() ↓ BaseDexClassLoader.loadClass() ↓ DexPathList.findClass() ↓ DexFile.loadClassBinaryName() └ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ┘ ↓ ┌ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ┐ 第五阶段:Application 创建 LoadedApk.makeApplication() ↓ Instrumentation.newApplication() ↓ Application.attach() ↓ Application.onCreate() └ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ┘ ↓ ┌ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ┐ 第六阶段:Activity 启动 ActivityThread.handleLaunchActivity() ↓ ActivityThread.performLaunchActivity() ↓ Instrumentation.newActivity() ↓ Activity.onCreate() └ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ┘ ↓ ┌ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ┐ 第七阶段:视图绘制 Activity.setContentView() ↓ PhoneWindow.setContentView() ↓ LayoutInflater.inflate() ↓ ViewRootImpl.performTraversals() ↓ measure() → layout() → draw() └ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ┘
so加载深入分析 Java层 Android 在 java 层加载 so 的接口是 System.loadLibrary()
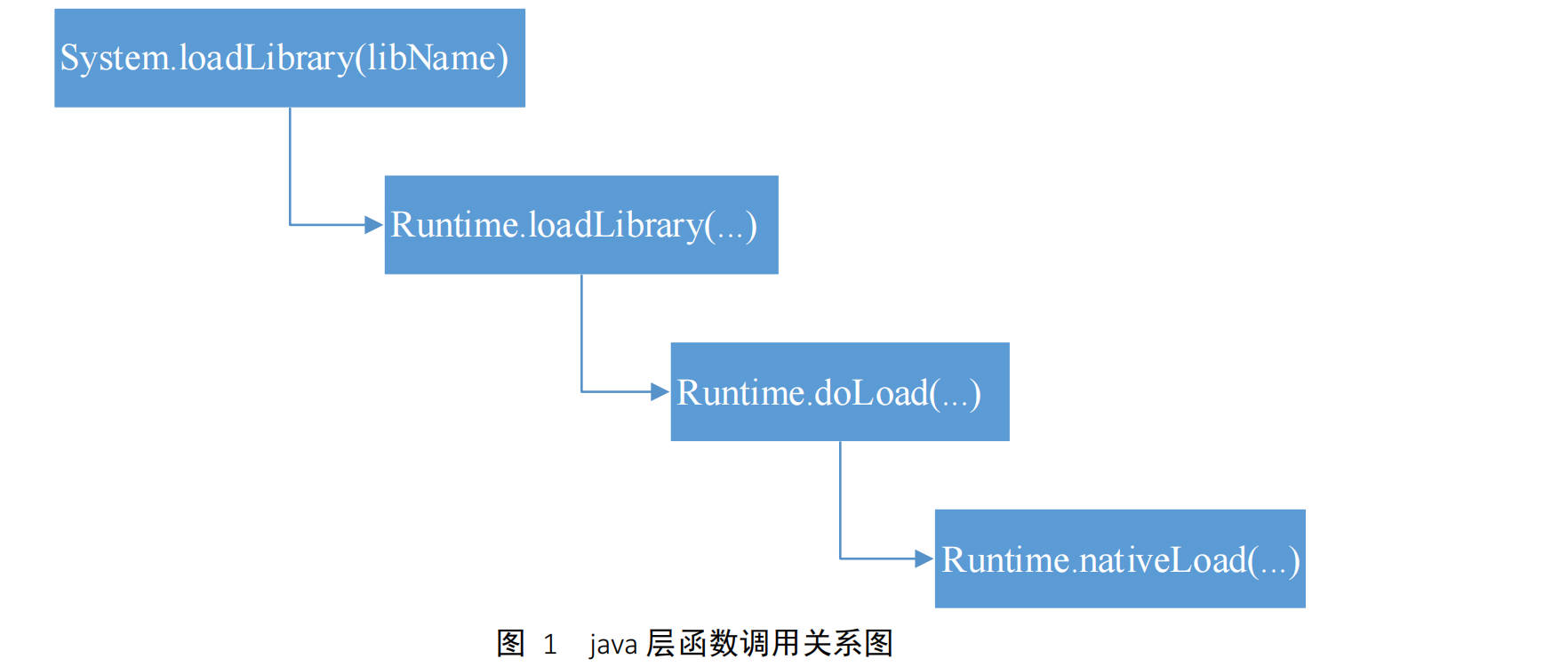
System.loadLibrary() 1 2 3 public static void loadLibrary (String libName) { Runtime.getRuntime().loadLibrary(libName, VMStack.getCallingClassLoader()); }
它是调用了 Runtime 类的 loadLibrary()
loadLibrary() 1 2 3 public void loadLibrary (String nickname) { loadLibrary(nickname, VMStack.getCallingClassLoader()); }
loadLibrary(String nickname) 调 用 了 它 的 一 个 重 载 函 数 loadLibrary(String libraryName, ClassLoader loader)
loadLibrary() 其关键代码如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 void loadLibrary (String libraryName, ClassLoader loader) { if (loader != null ) { String filename = loader.findLibrary(libraryName); ... String error = doLoad(filename, loader); ... return ; } ... }
获得 so 文件的绝对路径 filename,调用 doLoad()来加载 so 文件。
doLoad() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 private String doLoad (String name, ClassLoader loader) { String ldLibraryPath = null ; if (loader != null && loader instanceof BaseDexClassLoader) { ldLibraryPath = ((BaseDexClassLoader) loader).getLdLibraryPath(); } synchronized (this ) { return nativeLoad(name, loader, ldLibraryPath); } }
调用 nativeLoad()来加载 name 指向的.so 文件,nativeLoad()是 Runtime类的一个 native 函数,在 native 层对应的函数为 Runtime_nativeLoad()。
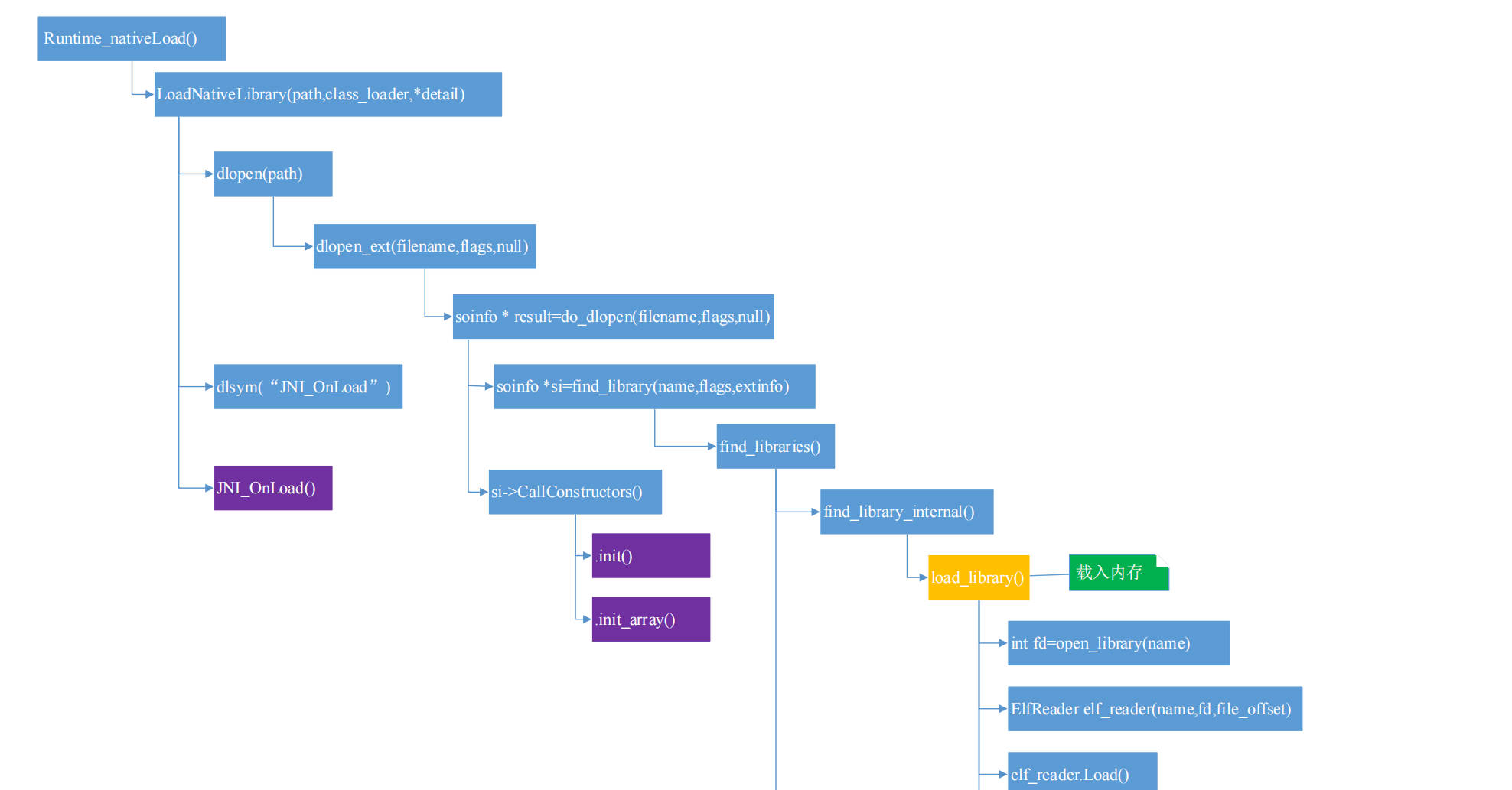
Native层 Runtime_nativeLoad() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 static jstring Runtime_nativeLoad (JNIEnv* env, jclass, jstring javaFilename, jobject javaLoader, jstring javaLdLibraryPath) ScopedUtfChars filename (env, javaFilename) ; if (filename.c_str () == nullptr ) { return nullptr ; } std::string detail; { ScopedObjectAccess soa (env) ; StackHandleScope<1> hs (soa.Self()) ; Handle<mirror::ClassLoader> classLoader ( hs.NewHandle(soa.Decode<mirror::ClassLoader*>(javaLoader))) JavaVMExt* vm = Runtime::Current ()->GetJavaVM (); bool success = vm->LoadNativeLibrary (filename.c_str (), classLoader, &detail); if (success) { return nullptr ; } } }
调用 JavaVMExt 类的 LoadNativeLibrary()函数来加载.so 文件,filename 是.so 文件的路径,detail 用于存储加载过程中的 log 信息。
LoadNativeLibrary() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 bool JavaVMExt::LoadNativeLibrary (const std::string& path, Handle<mirror::ClassLoader> class_loader, std::string* detail) detail->clear (); SharedLibrary* library; Thread* self = Thread::Current (); { MutexLock mu (self, libraries_lock) ; library = libraries->Get (path); } if (library != nullptr ) { if (library->GetClassLoader () != class_loader.Get ()) { StringAppendF (detail, "Shared library \"%s\" already opened by " "ClassLoader %p; can't open in ClassLoader %p" , path.c_str (), library->GetClassLoader (), class_loader.Get ()); LOG (WARNING) << detail; return false ; } ... if (!library->CheckOnLoadResult ()) { StringAppendF (detail, "JNI_OnLoad failed on a previous attempt " "to load \"%s\"" , path.c_str ()); return false ; } return true ; } self->TransitionFromRunnableToSuspended (kWaitingForJniOnLoad); const char * path_str = path.empty () ? nullptr : path.c_str (); void * handle = dlopen (path_str, RTLD_LAZY); ... self->TransitionFromSuspendedToRunnable (); ... bool created_library = false ; { MutexLock mu (self, libraries_lock) ; library = libraries->Get (path); if (library == nullptr ) { library = new SharedLibrary (path, handle, class_loader.Get ()); libraries->Put (path, library); created_library = true ; } } ... bool was_successful = false ; void * sym = nullptr ; if (UNLIKELY (needs_native_bridge)) { library->SetNeedsNativeBridge (); sym = library->FindSymbolWithNativeBridge ("JNI_OnLoad" , nullptr ); } else { sym = dlsym (handle, "JNI_OnLoad" ); } if (sym == nullptr ) { VLOG (jni) << "[No JNI_OnLoad found in \"" << path << "\"]" ; was_successful = true ; } else { typedef int (*JNI_OnLoadFn)(JavaVM*, void *); JNI_OnLoadFn jni_on_load = reinterpret_cast <JNI_OnLoadFn>(sym); ... int version = 0 ; { ScopedThreadStateChange tsc (self, kNative) ; VLOG (jni) << "[Calling JNI_OnLoad in \"" << path << "\"]" ; version = (*jni_on_load)(this , nullptr ); } ... } return was_successful; }
从上可知,LoadNativeLibrary()函数执行的主要流程为:判断该.so 文件是否已经加载了
如果已经加载了,检查class_loader 是否一样;
如果没有加载,调用 dlopen()函数加载该.so 文件;
调用 dlsym()找到 JNI_OnLoad 函数的地址;
调用 JNI_OnLoad 函数。
至此,一个.so 文件就加载完成了。
接下来了解一个.so 文件是如何载入内存、如何链接的。
dlopen() 1 2 3 void * dlopen (const char * filename, int flags) return dlopen_ext (filename, flags, nullptr ); }
dlopen()调用了dlopen_ext()。
dlopen_ext() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 static void * dlopen_ext (const char * filename, int flags, const android_dlextinfo* extinfo) ScopedPthreadMutexLocker locker (&g_dl_mutex) ; soinfo* result = do_dlopen (filename, flags, extinfo); if (result == nullptr ) { __bionic_format_dlerror("dlopen failed" , linker_get_error_buffer ()); return nullptr ; } return result; }
调用 do_dlopen() 来加载 filename 指向的.so 文件,返回值为 soinfo 对象的指针,因而 dlopen()函数的返回的指针指向一个 soinfo 对象。
do_dlopen() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 soinfo* do_dlopen (const char * name, int flags, const android_dlextinfo* extinfo) { ... protect_data (PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE); soinfo* si = find_library (name, flags, extinfo); if (si != nullptr ) { si->CallConstructors (); } protect_data (PROT_READ); return si; }
调用 find_library()函数得到 soinfo 的对象,然后调用si->CallConstructors()进行初始化。
先分析find_library()。
find_library() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 static soinfo* find_library (const char * name, int dlflags, const android_dlextinfo* extinfo) ... soinfo* si; if (!find_libraries (&name, 1 , &si, nullptr , 0 , dlflags, extinfo)) { return nullptr ; } return si; }
这里面调用了find_libraries()
find_libraries() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 static bool find_libraries (const char * const library_names[], size_t library_names_size, soinfo* soinfos[], soinfo* ld_preloads[], size_t ld_preloads_size, int dlflags, const android_dlextinfo* extinfo) LoadTaskList load_tasks; for (size_t i = 0 ; i < library_names_size; ++i) { const char * name = library_names[i]; load_tasks.push_back (LoadTask::create (name, nullptr )); } SoinfoLinkedList found_libs; size_t soinfos_size = 0 ; ... for (LoadTask::unique_ptr task (load_tasks.pop_front ()); task.get () != nullptr ; task.reset (load_tasks.pop_front ())) { soinfo* si = find_library_internal (load_tasks, task->get_name (), dlflags, extinfo); ... soinfo* needed_by = task->get_needed_by (); if (is_recursive (si, needed_by)) { return false ; } si->ref_count++; if (needed_by != nullptr ) { needed_by->add_child (si); } found_libs.push_front (si); ... if (soinfos_size < library_names_size) { soinfos[soinfos_size++] = si; } } soinfo* si; while ((si = found_libs.pop_front ()) != nullptr ) { if ((si->flags & FLAG_LINKED) == 0 ) { if (!si->LinkImage (extinfo)) { return false ; } si->flags |= FLAG_LINKED; } } ... return true ; }
find_libraries()将数组 library_names[]中的 so 文件加载到内存,并进行链接。这里将 find_libraries()分为三个部分来进行分析。第一部分:初始化阶段;第二部分:采用宽度优先搜索加载 so;第三部分:对加载的 so 进行链接。
初始化阶段 要加载的 so 可能依赖于其他库,linker 采用宽度优先搜索依次加载 so 及其依赖库。搜索树中父节点的依赖库为其子节点,根节点是待加载的.so 文件。
load_tasks 是用于宽度优先搜索的栈,对其进行初始化。found_libs 是.so 文件和其依赖库的列表。
载入 so 到内存 这部分对.so 文件及其依赖库按照宽度优先的顺序依次进行加载,最关键的是调用 find_library_internal()函数,用于加载 so。
find_library_internal() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 static soinfo* find_library_internal (LoadTaskList& load_tasks, const char * name, int dlflags, const android_dlextinfo* extinfo) soinfo* si = find_loaded_library_by_name (name); if (si == nullptr ) { TRACE ("[ '%s' has not been found by name. Trying harder...]" , name); si = load_library (load_tasks, name, dlflags, extinfo); } return si; }
find_library_internal()首先会检查 name 指向的.so 是否已经加载,如果没有,就调用 load_library()加载。
load_library() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 static soinfo* load_library (LoadTaskList& load_tasks, const char * name, int dlflags, const android_dlextinfo* extinfo) int fd = -1 ; off64_t file_offset = 0 ; ScopedFd file_guard (-1 ) ; if (extinfo != nullptr && (extinfo->flags & ANDROID_DLEXT_USE_LIBRARY_FD) != 0 ) { ... } else { fd = open_library (name); ... } if ((file_offset % PAGE_SIZE) != 0 ) { ... return nullptr ; } struct stat file_stat; if (TEMP_FAILURE_RETRY (fstat (fd, &file_stat)) != 0 ) { ... return nullptr ; } for (soinfo* si = solist; si != nullptr ; si = si->next) { if (si->get_st_dev () != 0 && si->get_st_ino () != 0 && si->get_st_dev () == file_stat.st_dev && si->get_st_ino () == file_stat.st_ino && si->get_file_offset () == file_offset) { TRACE ("library \"%s\" is already loaded under different name/path \"%s\" - will return existing soinfo" , name, si->name); return si; } } ElfReader elf_reader (name, fd, file_offset) ; if (!elf_reader.Load (extinfo)) { return nullptr ; } ... soinfo* si = soinfo_alloc (SEARCH_NAME (name), &file_stat, file_offset); if (si == nullptr ) { return nullptr ; } si->base = elf_reader.load_start (); si->size = elf_reader.load_size (); si->load_bias = elf_reader.load_bias (); si->phnum = elf_reader.phdr_count (); si->phdr = elf_reader.loaded_phdr (); if (!si->PrelinkImage ()) { soinfo_free (si); return nullptr ; } for_each_dt_needed(si, [&] (const char * name) { load_tasks.push_back (LoadTask::create (name, si)); }); return si; }
将 load_library()分为三个部分来进行分析。第一部分:主要作用是打开.so 文件,并判断是否已经加载;第二部分:加载.so文件的可加载段;第三部分:创建 soinfo 对象,解析.dynamicsection,并将该.so 文件的依赖库添加到待加载的队列中。
打开 so 文件 内存 页 的 大 小 PAGE_SIZE 为 4096 , 定 义 位 于 头文件/bionic/libc/include/limits.h,现在最好通过 sysconf(_SC_PAGE_SIZE)来获取 PAGE_SIZE 的值,sysconf()位于/bionic/libc/bionic/sysconf.cpp,从sysconf 的实现可以知道,sysconf(_SC_PAGESIZE)也可以用来获取 PAGE_SIZE 的值。然后检查.so 文件是否以不同的文件名被加载过了。Linux 下一个文件可以有多个链接文件,因而不同的文件名可能指向的是同一个文件。
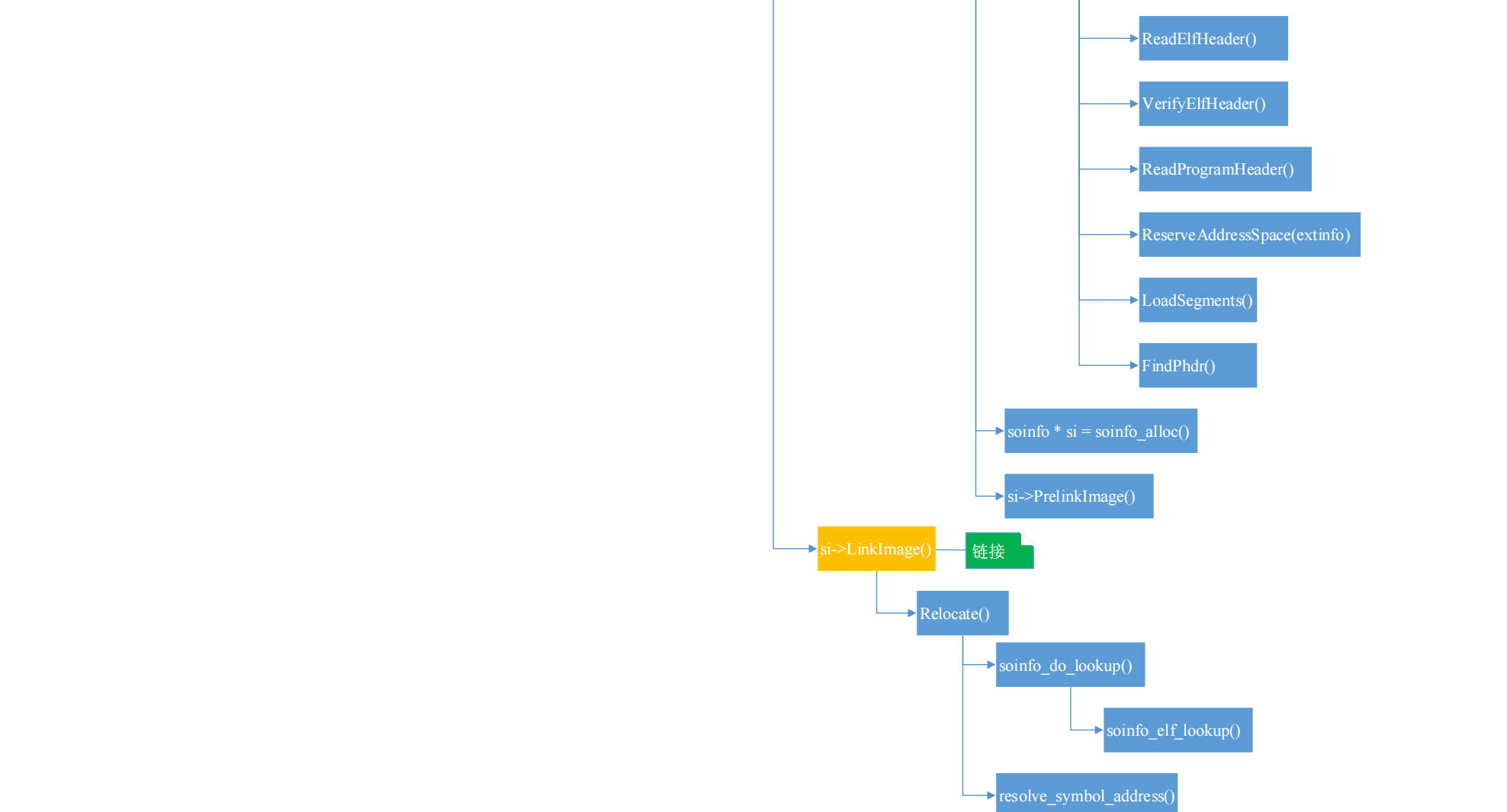
映射 so 文件到内存 用 ElfReader 类解析 ELF 头,并根据 program header table加载段。其成员函数 Load()实现如下:
Load()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 bool ElfReader::Load (const android_dlextinfo* extinfo) return ReadElfHeader () && VerifyElfHeader () && ReadProgramHeader () && ReserveAddressSpace (extinfo) && LoadSegments () && FindPhdr (); }
**ReadElfHeader()**用于读取 ELF 的头,并将结果赋给 ElfReader 的成员变量Elf32_Ehdr header_,Elf32_Ehdr 的定义可以在/art/runtime/elf.h 中找到,自动生成的文件/bionic/libc/kernel/uapi/linux/elf.h 中也有相关 elf 的定义。
**VerifyElfHeader()**用于检查 ELF 头某些字段是否合法。
**ReadProgramHeader()**将 program header table 从.so 文件通过 mmap64 映射到只读私有匿名内存。
**ReserveAddressSpace()**通过 mmap 创建足够大的匿名内存空间,以便能够容纳所有可以加载的段
LoadSegments()
遍历 program header table,找到可加载段,并通过 mmap 将可加载段从文件映射到内存。
FindPhdr()
检查 program header table 是否已经在内存中了,即检查可加载段中是否包含 program header table。
解析 dynamic section load_library()函数中创建一个了 soinfo 对象,并对相关字段进行赋值:
1 2 3 4 5 si->base:加载 so 文件时,mmap 得到的内存空间的首地址。 si->size:ReserveAddressSpace 中开启的内存空间的大小; si->load_bias : 加载的偏移地址, 对 于 一个可加载段来说,si->load_bias+p_vaddr 是它在内存中的地址; si->phnum:program header 的个数; si->phdr:program header table 在内存中的起始地址。
调用 PrelinkImage()解析.so 文件的.dynamic section;将该.so 文件依赖的库添加到待加载的队列中。
在分析 PrelinkImage()之前,先看一下.dynamic section 中 entry 的数据结构,如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 struct Elf32_Dyn { Elf32_Sword d_tag; union { Elf32_Word d_val; Elf32_Addr d_ptr; } d_un; };
略写
链接阶段 对加载的 so 进行链接操作,链接的顺序与加载的顺序刚好相反。
调用 LinkImage()进行链接
LinkImage() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 bool soinfo::LinkImage (const android_dlextinfo* extinfo) #if !defined(__LP64__) if (has_text_relocations) { DL_WARN ("%s has text relocations. This is wasting memory and prevents " "security hardening. Please fix." , name); if (phdr_table_unprotect_segments (phdr, phnum, load_bias) < 0 ) { DL_ERR ("can't unprotect loadable segments for \"%s\": %s" , name, strerror (errno)); return false ; } } #endif #if defined(USE_RELA) ... #else if (rel != nullptr ) { DEBUG ("[ relocating %s ]" , name); if (Relocate (rel, rel_count)) { return false ; } } if (plt_rel != nullptr ) { DEBUG ("[ relocating %s plt ]" , name); if (Relocate (plt_rel, plt_rel_count)) { return false ; } } #endif DEBUG ("[ finished linking %s ]" , name); #if !defined(__LP64__) if (has_text_relocations) { if (phdr_table_protect_segments (phdr, phnum, load_bias) < 0 ) { DL_ERR ("can't protect segments for \"%s\": %s" , name, strerror (errno)); return false ; } } #endif if (phdr_table_protect_gnu_relro (phdr, phnum, load_bias) < 0 ) { DL_ERR ("can't enable GNU RELRO protection for \"%s\": %s" , name, strerror (errno)); return false ; } return true ; }
对.rel.dyn 和.rel.plt 两个重定位表都是调用Relocate()来进行重定位的。在分析 Relocate()之前,先看一下重定位表项的数
据结构
略写
链接完成后 so 文件加载到内存,并链接完成后,就开始调用 so 中的初始化函数。
回到 do_dlopen()继续分析:
在do_dlopen()中调用 CallConstructors()进行初始化操作。
CallConstructors() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 void soinfo::CallConstructors () if (constructors_called) { return ; } ... get_children ().for_each([] (soinfo* si) { si->CallConstructors (); }); ... CallFunction ("DT_INIT" , init_func); CallArray ("DT_INIT_ARRAY" , init_array, init_array_count, false ); }
CallConstructors() 主 要 是 执 行 了 两 段 初 始 化 代 码 : init_func 和init_array,这两个变量是在 PrelinkImage()中解析 dynamic section 时赋值的。通常加壳逻辑就放在 init_func 或 init_array 中,它们先于 jni_onLoad 执行。
至此,完成了 so 的加载分析。
native 层函数调用关系图